Ever wondered where great white sharks get to when they’re not peering in at cage divers or dining on hapless seals? Well, the answer is on the OCEARCH website: for several years now, great whites and other apex predator sharks have been tagged and their locations recorded every time they surface and send a ‘ping’ to the satellite tracking system.
It’s a fascinating glimpse into the lives of these magnificent creatures: there are tagged populations off the East Coast of the United States, the West Coast of South America, and the South African coast. The researchers have named all the sharks, and my favourite is Lydia, a great white shark.

Lydia being tagged on 2 March 2013, off the coast at Jacksonville, Florida, United States. At the time of tagging she was 4.40 m (14 ft 6 in) long and weighed approximately 900 kg (approx. 2,000 lbs).
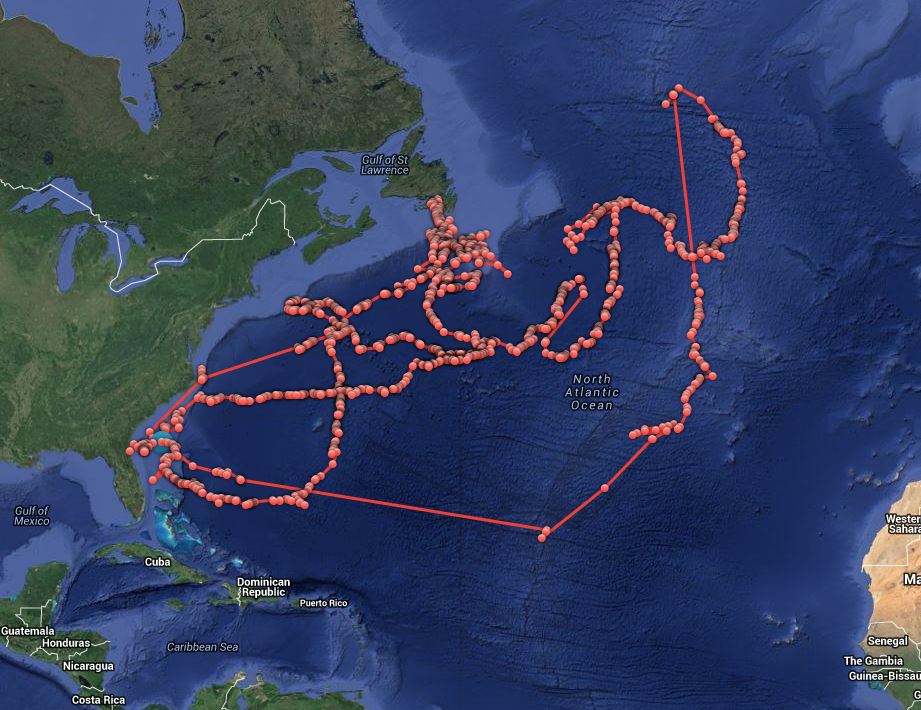
Lydia is a very well-travelled shark: earlier this year she headed east from the eastern seaboard of the US to the middle of the Atlantic. To the very middle, in fact: for several weeks in March and April she swam down the line of the Mid Atlantic Ridge.
It’s fascinating to see where the sharks go, and how far and how quickly they travel.
OCEARCH is a wonderful organisation, undertaking research vital for the conservation of these beautiful creatures. Here’s a little about them, from their website:
‘OCEARCH enables the brightest scientists in the world by giving them approximately 15 minutes of access to live, mature great white sharks (and other species) to conduct up to 12 studies including tagging and sampling. OCEARCH captures mature sharks that can range between 2,000 and 5,000 pounds on average, maneuvers them onto a 75,000 lb. custom lift, then releases the shark after researchers have completed their 15 minutes of work. The shark is guided by hand in the water on and off the lift. OCEARCH is a leader in collaborative open source research, sharing scientific data and dynamic education content in near-real time for free to the public through the Global Shark Tracker, enabling students and the public to learn alongside PhDs.’
Hurrah for OCEARCH, and hurrah for open source research: it’s not just the scientists who benefit.