Mary Russell Thew (1876—1953, née Mary Russell Frew) was a Scottish Arts and Crafts jeweller, perhaps best known for her free-flowing use of silver wire, with trails and beads, as well as using materials such as abalone and cabochon semi-precious gemstones. Her work is in the collections of the Victoria and Albert Museum in London.

Mary Thew. Partly gilded silver brooch with abalone, jade, turquoise and citrine. In the collections of the V&A.
Mary was born in Hillhead in Glasgow in 1876. She studied for a short time at the Glasgow School of Art in the mid 1890s, becoming friends there with Jessie Marion King and Jessie’s husband E.A. Taylor, before marrying her husband, James Mursell Thew, in 1903. James was an engineer, and enjoyed silversmithing as a hobby and making pieces for Mary; she soon began making designs herself. James died after only a few years of marriage, and with a young son to support, Mary decided to turn her hobby into her career. She took a short course of four lessons in jewellery making from famed Arts and Crafts jeweller Rhoda Wager, who had also studied at the Glasgow School. This must have been some time before 1913, as after that date Wager emigrated, first to Fiji and then to Australia, where she was to live for the rest of her life. Mary became a member of the ‘Greengate Close Coterie’, a group of friends and artisans who came to live for extended periods in the village of Kirkcudbright, where King and Taylor had settled in 1915. From 1911 Mary was a member of the Glasgow Society of Lady Artists, and she won the Society’s Lauder Award for a case of jewellery in 1925. She also exhibited at the Walker Art Gallery in Liverpool. An undated jewellery box of Mary’s is marked ‘Mary R. Thew, 704 Anniesland Road, Glasgow W.4.’ She also lived in Helensburgh at some point in her life.

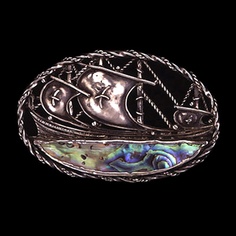
Mary Thew. Silver brooch with a galleon design, set with freshwater pearls, amethysts and citrines. Sold by Tadema Gallery. Source: Zorn Karlin 1993, 143.
Mary took much inspiration from the jewellery of foreign countries whenever she travelled. She also designed Celtic-inspired pieces, as well as making jewellery with the popular Arts and Crafts galleon motif. Her freeform wirework pieces are perhaps her most iconic, though: trails and beads of wire wrapped to form a circular frame, on which are mounted cabochon semi-precious stones or abalone plaques or freshwater pearls.

Attributed by the sellers to Sibyl Dunlop, but I am pretty sure this is by Mary Thew. Moonstone and Biwa pearls wirework brooch, with what looks like gilded silver (hard to tell as the photo isn’t the best). Sold by Dreweatts & Bloomsbury.
In 1939 Mary was living in Milngavie, a small town some 10 km (6 miles) north-west of Glasgow. Here Nan Muirhead Moffat, a newspaper reporter, described her workshop:
The desk is surmounted by shelves from which hang the numerous tools required for this complicated craft. The jeweller sits on a high Windsor chair … Within easy reach are her bottle of sperm oil and sulphuric acid, borax (used as a flux), a polishing lathe, a rolling machine, a vice, and a sandbag for hammering repousse. In the sketch, the artists is shown revolving a ring, on a wire ‘wig’, in a Bunsen-burner flame, while she uses foot bellows. While working, she always wears a leather apron and another is fixed under the desk to catch any jewels or pieces of metal which might be dropped.
The reporter then went to look at Mary’s jewellery:
Brooches, pendants, rings, ear-rings, chains, bracelets, buckles and links shimmered and glowed in the afternoon sunshine. I also saw beautiful crosses, showing Celtic influence, with characteristic inter-lacings and whorls, and I admired silver butter-forks, spoons and key-rings.

Mary Thew. Matrix turquoise and silver Celtic cross pendant, signed on the back with Mary’s punched ‘T’ mark. Her signed pieces are very rare. For sale on Etsy: click on photo for details.

Mary Thew opal and pearl-decorated Celtic cross. No mention in the description if it was signed on the back. Sold in 2006 by Lyon and Turnbull.
Mrs Thew told me that once she had to make silver hinges for an old book, belonging to Professor Latts, the cracked covers of which were made from the wood of an old battleship. Recently she had been making a great many hand-wrought silver tops for the fashionable embroidered handbags. She had also made copies, to order, of antique jewellery.
The artist has an instinct for creating a pleasing balance between space and decoration in her work, and she has a fine colour sense. She neither overloads with ornamentation nor allows her devotion to detail to detract from the general effect of her design.
Entrancing treasures
In the drawers a heterogeneous collection of gems from all over the world was mixed in an entrancing disorder—American jade from Salt Lake City, Scottish pearls, Connemara marble, New Zealand shells, Mexican fire opals, corals, malachite, crystals, moss-agates, green pebbles, and magic moonstones.

Mary Thew. Silver, abalone and freshwater pearl brooch. Sold by Tadema Gallery. Source: Zorn Karlin 1993, 143.
Mary Thew didn’t often sign her work, but when she did it was usually in the form of a ‘T’ punched on to the back of the piece.

Celtic cross pendant signed by Mary Thew: a ‘T’ made of punched dots, punched through from the other side before the matrix turquoise stone was set. Signed pieces are very rare. For sale on Etsy: click on photo for details.
Her work is now very sought-after, and is sold by specialist jewellery galleries in London such as Tadema Gallery and Van Den Bosch.
I was very lucky to find an unattributed Mary Thew brooch, which I sold in my Etsy shop. It wasn’t signed but had the characteristics of her work, including freeform wirework, trails and beads, as well as an abalone plaque. The Director of Decorative Arts at Lyon and Turnbull in Edinburgh corroborated my identification. The day I found that brooch was a very special one indeed, and for a short while I was the proud possessor of a Mary Thew masterpiece! I’m pleased to report that it has since returned to Scotland, its ancestral home.

Mary Thew silver and abalone brooch, sold on eBay in November 2015 and a companion piece to my brooch.
Given the wide range of jewellery types that Mary Thew made, as mentioned in the 1939 article, it would be wonderful to see more examples of her non-brooch jewellery. Tadema Gallery has sold a bracelet of hers, but apart from that, and the two Celtic cross pendants above, the only pieces of which I have seen records have all been brooches. (The pendant/necklace below was made recently, using a Mary Thew brooch.)

Mary Thew. Silver, jade, goshenite and pearl pendant and necklace, made using the original brooch below and sold by Tadema Gallery.

Mary Thew. Silver and opal doublet bracelet. Sold by Tadema Gallery. (Looks like lapis lazuli, but I assume that’s the colour reproduction).

An art glass faux turquoise and silver pendant, attributed to Mary Thew. For sale in my Etsy shop, Inglenookery: click on photo for details.
Mary was also a talented artist and musician. She died in 1953 in North Wales.
Sources: Jewelry and Metalwork in the Arts and Crafts Tradition by Elyse Zorn Karlin, 1993, 142-3; ‘Round the Studios: 7. Mrs Mary Thew – Jeweller’ by Nan Muirhead Moffat, The Glasgow Herald, 18 May 1939, 8; Mary Thew entry at the In the Artists’ Footsteps website; Mary Thew entry in Artists in Britain Since 1945—Chapter T by the Goldmark Gallery.
Further reading: Glasgow Style by Gerald and Celia Larner, Paul Harris Publishing, Edinburgh, 1979; Glasgow Girls: Women in Art and Design 1880—1920 edited by Jude Burkhauser, Canongate, Edinburgh, 1990; Tales of the Kirkcudbright Artists by Haig Gordon, Galloway Publishing, Kirkcudbright, 2006; Glasgow Girls: Artists and Designers 1890—1930 by Liz Arthur, Kirkcudbright, 2010.